Soil EC & Crop Growth
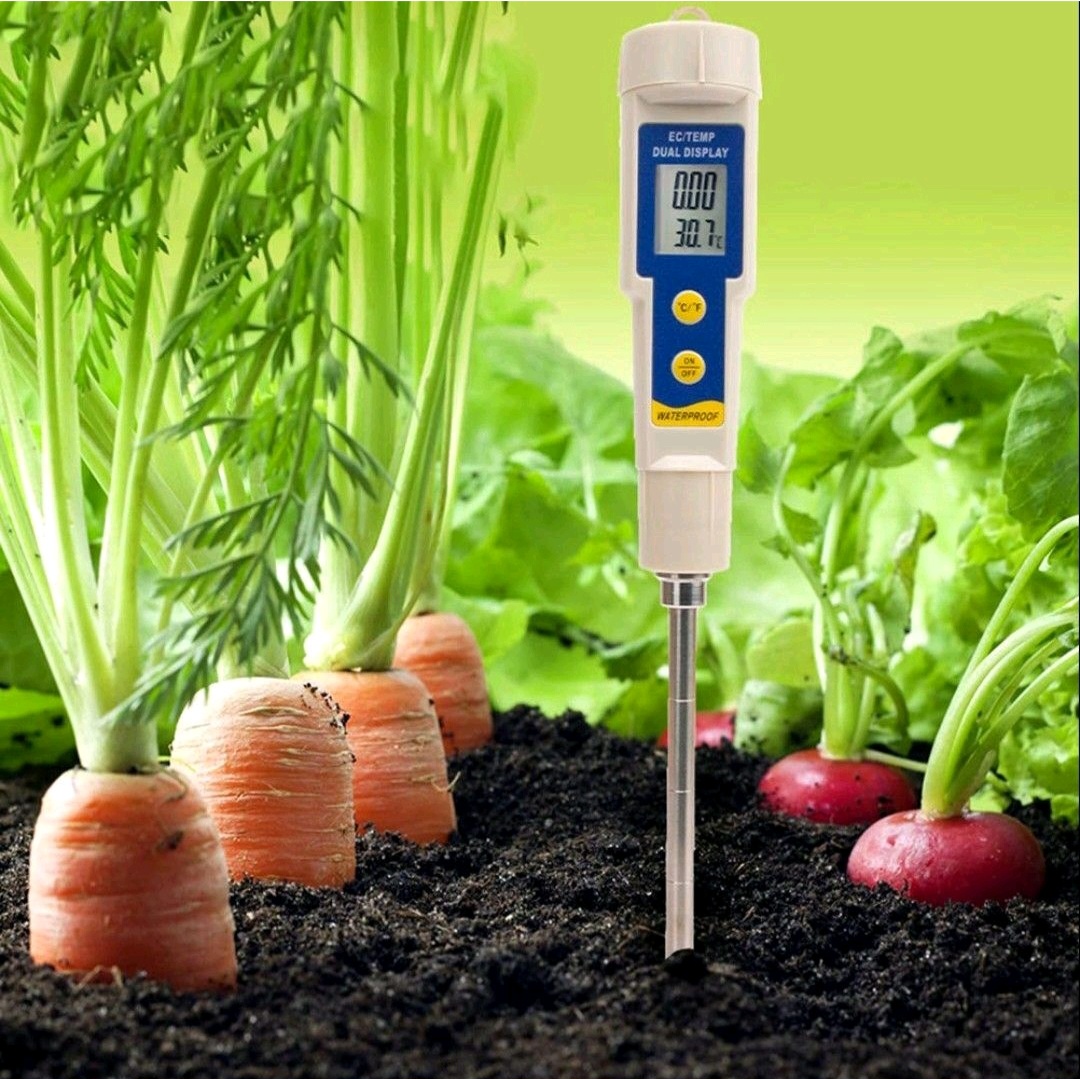
🔹 Agricultural soil EC: (Electrical Conductivity) refers to the measure of the soil’s ability to conduct electrical current. It provides information about the salt content and overall fertility of the soil. The EC value indicates the concentration of dissolved salts in the soil solution.
🔹 Measurement of soil EC: is typically done using a device called an EC meter or a conductivity meter. The meter measures the electrical conductivity between two electrodes inserted into the soil. The reading is usually provided in deciSiemens per meter (dS/m) or milliSiemens per meter (mS/m).
🔹 The ideal soil EC: for better crop growth varies depending on the specific crop and environmental conditions. However, in general, a low to moderate soil EC is considered ideal. Most crops thrive in soils with EC values ranging from 0.5 to 3.0 dS/m. Extremely low EC levels can indicate nutrient deficiencies, while high EC levels can negatively affect crop growth and yield.
Effect of Soil EC on fertility & crop growth:
🔹 Nutrient availability: High EC levels can lead to increased salinity, which can interfere with the uptake of essential nutrients by plant roots. This can result in nutrient imbalances and deficiencies, limiting crop growth.
🔹 Soil structure: Excessive salinity can cause soil particles to bind together, leading to soil compaction and reduced water infiltration. This affects root penetration and restricts the plant’s access to water and nutrients.
🔹 Osmotic stress: High EC levels create an osmotic imbalance between the soil solution and plant roots, causing water to move out of the plant. This leads to water stress and reduced crop productivity.
Measures to be taken to maintain the ideal soil EC:
🔹 Regular Soil testing: To monitor changes over time and detect any significant deviations from the desired range.
🔹Implement Proper irrigation management: Such as drip irrigation or precision irrigation to minimize salt accumulation and leach excess salts from the root zone.
🔹 Balanced nutrient management: Apply fertilizers based on soil nutrient tests to ensure proper nutrient balance and minimize the risk of salt accumulation.
🔹 Improve Soil Drainage management: To prevent waterlogging and reduce the potential for salt buildup.
🔹Rotate crops and incorporate cover crops: That have salt-tolerant properties to help reduce soil salinity levels.
🔹 Organic matter addition: Into the soil, such as compost or crop residues, to improve soil structure, water-holding capacity, and nutrient availability.
By implementing these measures, farmers can help maintain an ideal soil EC, ensuring optimal soil fertility and promoting healthy crop growth. It is essential to consider the specific crop requirements, regional conditions, and consult with agricultural expert services for customized recommendations.
© Rahul Padwal
Pune – India 🇮🇳
#agriculture #organicfarming #soilhealth #sustainableagriculture
Image by google