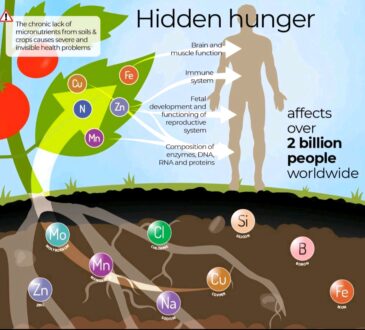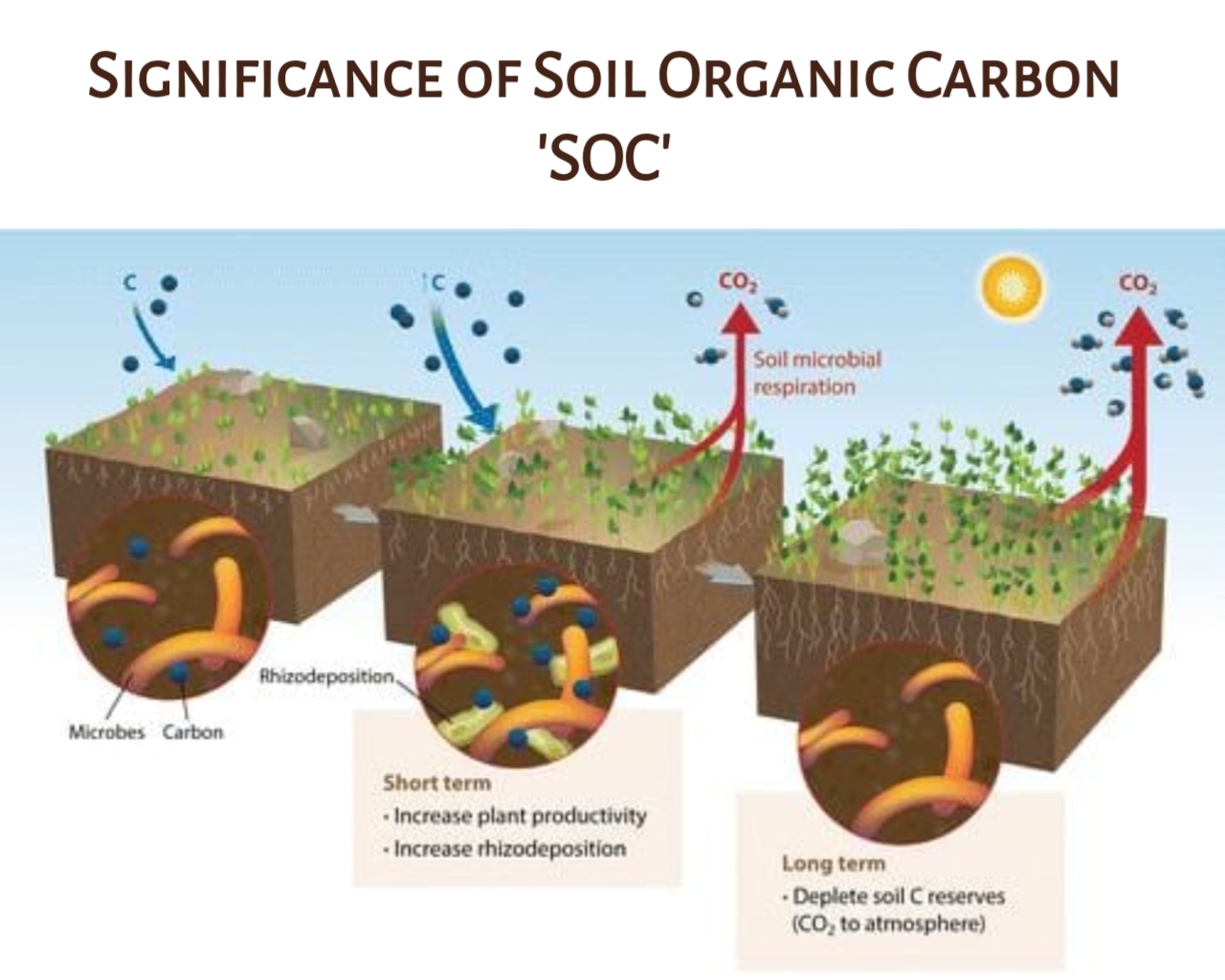
Soil Organic Carbon: SOC refers to the carbon content present in the organic matter of the soil, such as dead plant and animal materials in various stages of decomposition.
Crucial Role of SOC in Crop Production:
Nutrient Cycling: SOC acts as a reservoir of nutrients, including nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur. It undergoes decomposition by soil microorganisms, releasing these essential nutrients for plant uptake, thereby supporting crop growth.

Soil Fertility: SOC is vital for maintaining soil fertility. It enhances the cation exchange capacity of the soil, allowing it to retain and supply nutrients to plants. Additionally, organic matter contributes to a favorable soil pH and provides favorable conditions for beneficial soil organisms.
Water Retention and Drainage: SOC improves soil structure, enhancing its ability to hold water. Soils rich in organic carbon can retain moisture, ensuring better water availability for plants during dry periods. Moreover, it promotes proper drainage, preventing waterlogging and associated problems.
Soil Erosion Prevention: Soils with adequate SOC have improved aggregate stability, reducing erosion caused by wind and water. The organic matter binds soil particles together, preventing them from being carried away by erosive forces.
🚫 Unfortunately, soil organic carbon levels have been decreasing globally due to various reasons, mainly intensive farming practices like excessive tillage, monocropping, and overuse of chemical fertilizers and pesticides can accelerate the breakdown of organic matter and decrease SOC levels.
To increase soil organic carbon levels, several management practices can be adopted:
Organic Matter Addition: Incorporate organic materials, such as compost, crop residues, green manure, or animal manure, into the soil. These inputs enhance SOC content and provide additional nutrients.

Minimize Chemical Inputs: Reduce the excessive use of chemical fertilizers & pesticides, as they can negatively affect soil organisms responsible for organic matter decomposition.

Conservation Tillage: Reduce or eliminate tillage operations to minimize disturbance to the soil structure and decrease organic matter decomposition.
Crop Rotation & Diversification: Planting diverse crops and implementing crop rotation helps maintain and enhance SOC levels. Different plants contribute varying amounts and types of organic matter to the soil.
Cover Crops: Planting cover crops during fallow periods or between cash crop seasons can protect the soil, prevent erosion, and increase organic matter inputs.

Overall, adopting sustainable soil management practices that prioritize the preservation and enhancement of organic matter is key to increasing and maintaining soil organic carbon levels for long-term soil health and sustainable crop production.
© Rahul Padwal
Pune, India 🇮🇳
#soilhealth #organicfarming #sustainableagriculture
(image by google)